- Home
- Spaceplanes
- Spacecraft
- Space Tourism
- Transport
- Our Astronauts
- Moon
- Mars
- FAQs
- News | Library
- About us
Launching Astronauts | Space Travelers Extraordinaire
Launching Astronauts are the first 500 individual Space tourists and Space Travelers who book an Orbital Cruise or Sub-Orbital Zero-G flight. They are the only individuals (besides Titans and Guest Astronauts) who can book cruises and flights until 2031 – bookings are otherwise reserved for groups only.
Become an Astronaut
Spaceplane Cruises & Flights
Special Space &
Aerospace Perks
Only Individual Opportunity until 2031
Included in Future Stock Option Plan
Index | Low-Earth Orbit Travel
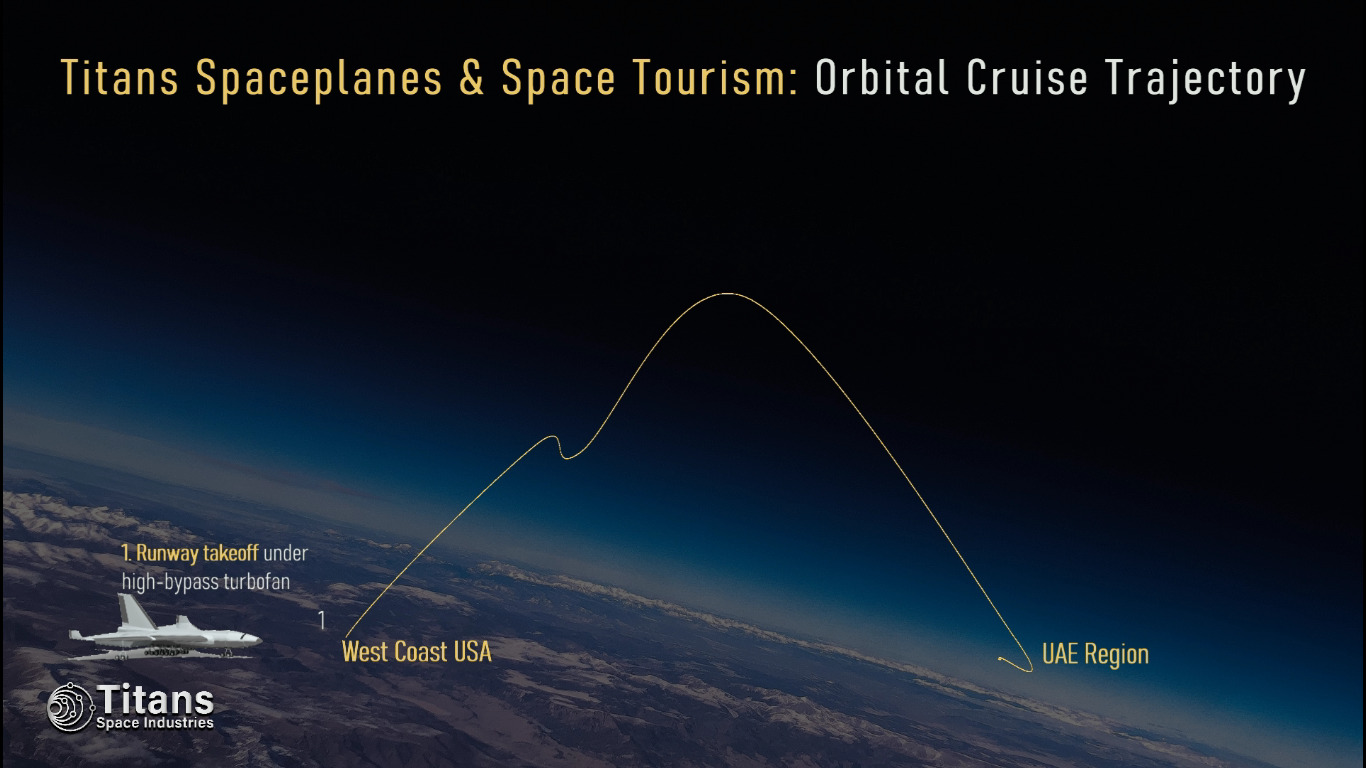
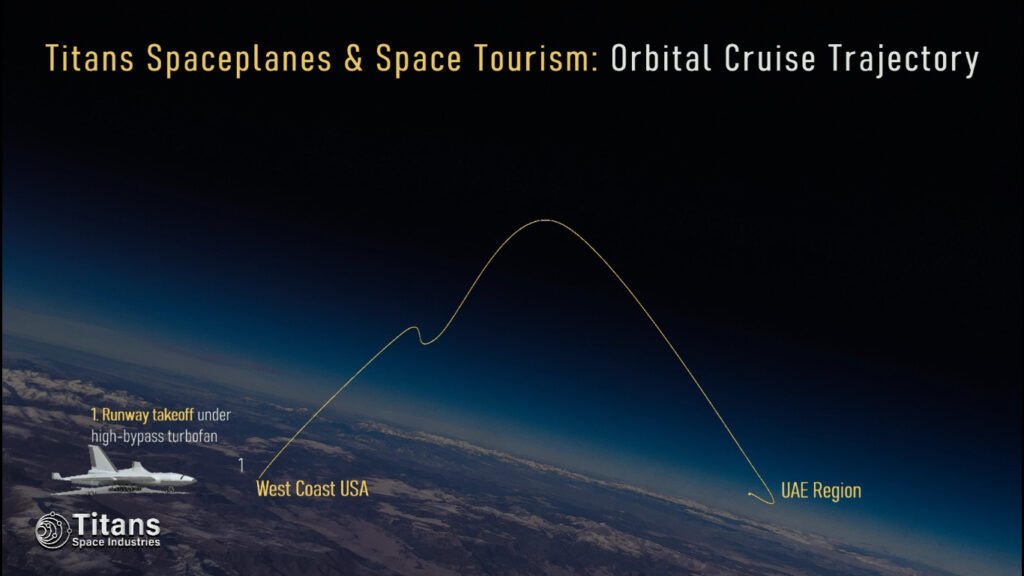
Titans Space’s single-stage-to-orbit spaceplanes will facilitate affordable Orbital Cruises and Sub-Orbital Zero-G Flights for space tourism purposes as well as ultra-fast point-to-point transportation for humans and cargo.

Launching Astronauts booking an Orbital Cruise will also receive a corresponding Sub-Orbital Zero-G booking. For example, a Platinum Orbital Cruise booking will include a Platinum Sub-Orbital Zero-G flight.
The Launching Astronauts offer is valid until December 2024 or until the first 500 Launching Astronauts are booked, whichever comes first.

Titans Space Industries (TSI) operates Orbital Cruises, and its spin off company, Titans Sub-Orbital (TSO) operates the Sub-Orbital tourism and travel flights.
Launching Astronauts are automatically enrolled in a future Titans Sub-Orbital company Stock Options offering, making them co-owners of TSO.

Despite the media hype surrounding rockets like SpaceX’s Starship, routine space transportation, including human space travel, by means of rockets will not reach large numbers, basically due to the inherent risks and limitations of such vehicles.
For large scale space tourism and travel to reach efficiency and safety levels like air travel/air cargo, the vehicles we use must operate like airplanes.
Titans Spaceplanes are the holy grail of aerospace; they are designed as a revolutionary space transportation system that eliminates the need for expensive launch facilities, vehicle assembly buildings, and (expendable or reusable) all-rocket boosters.
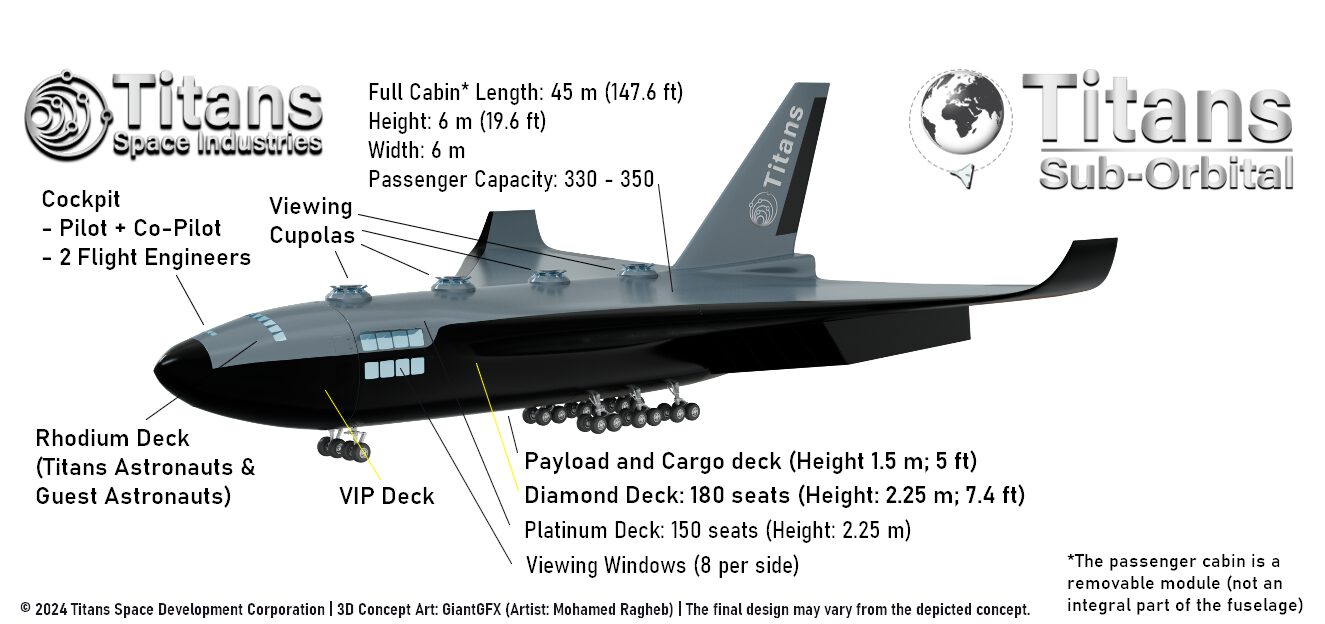
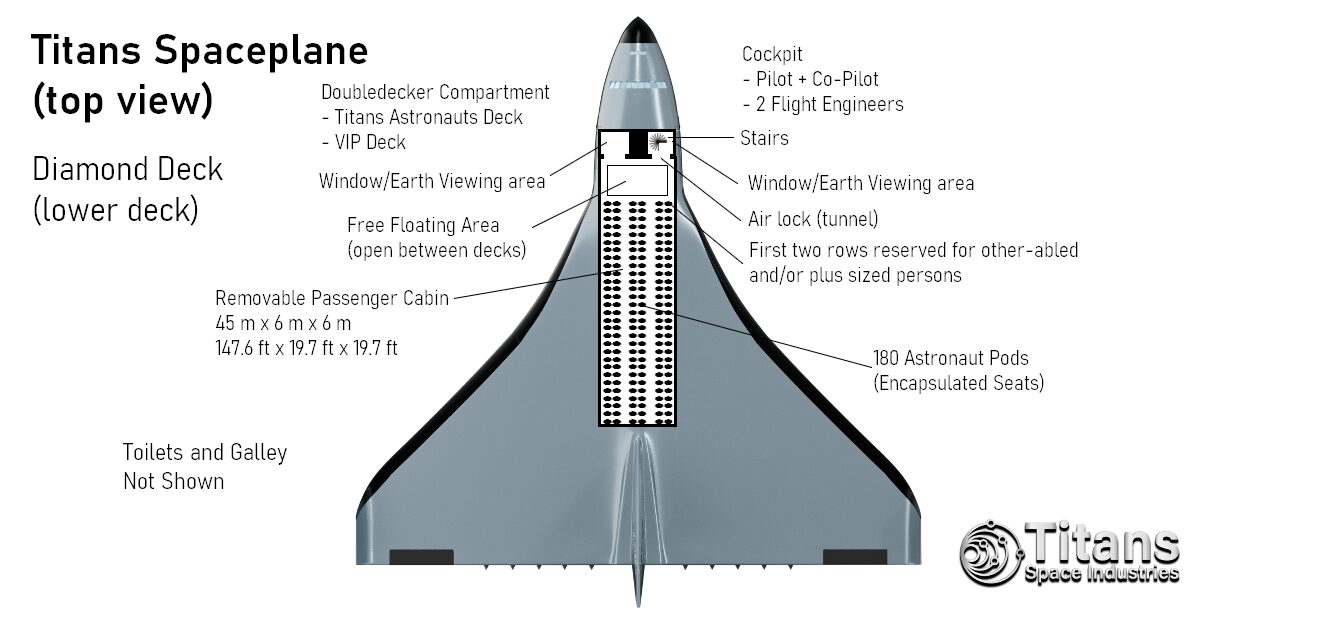
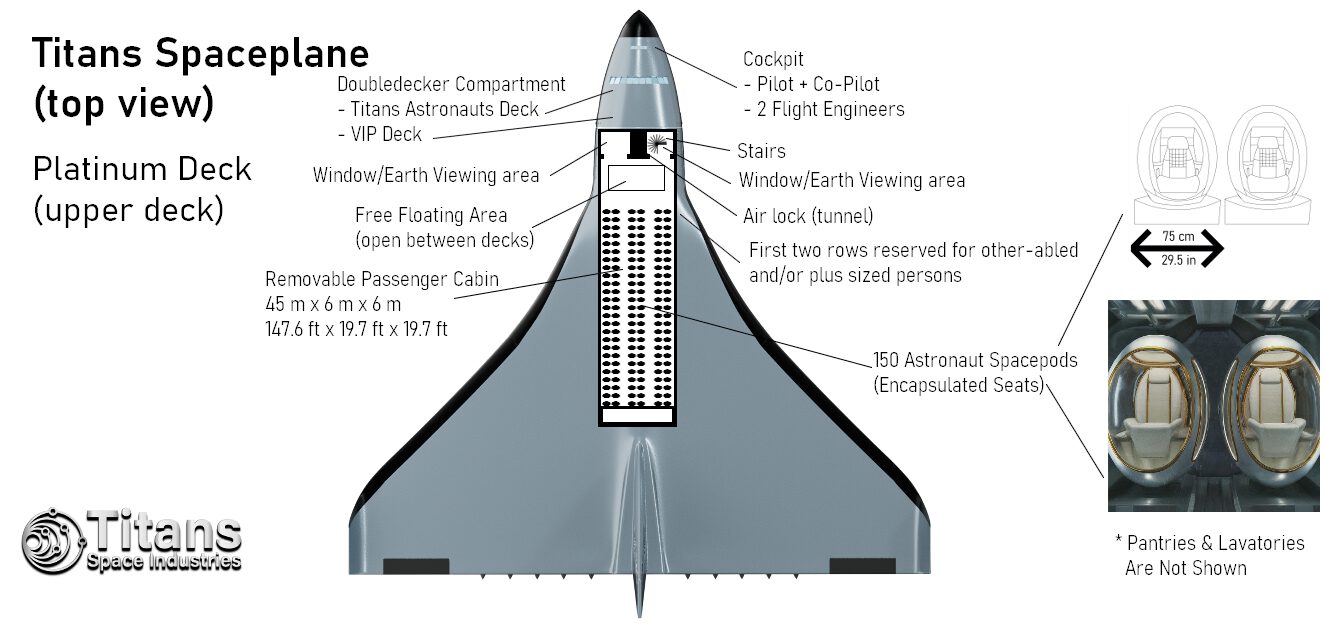
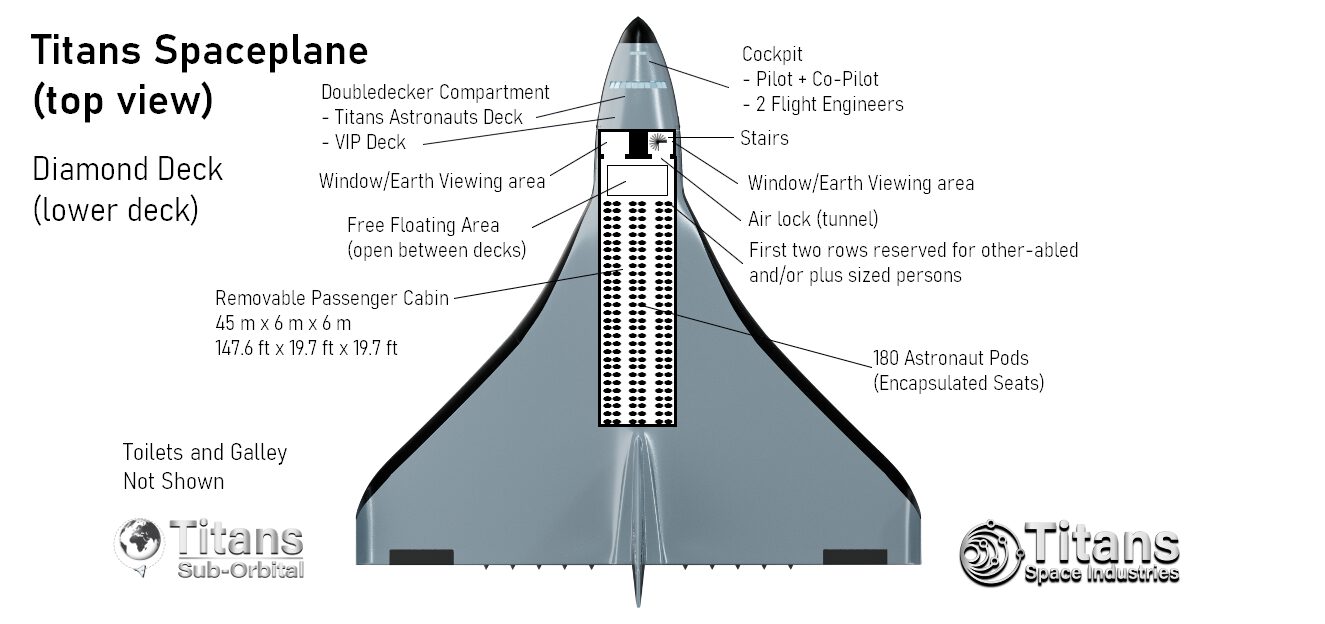
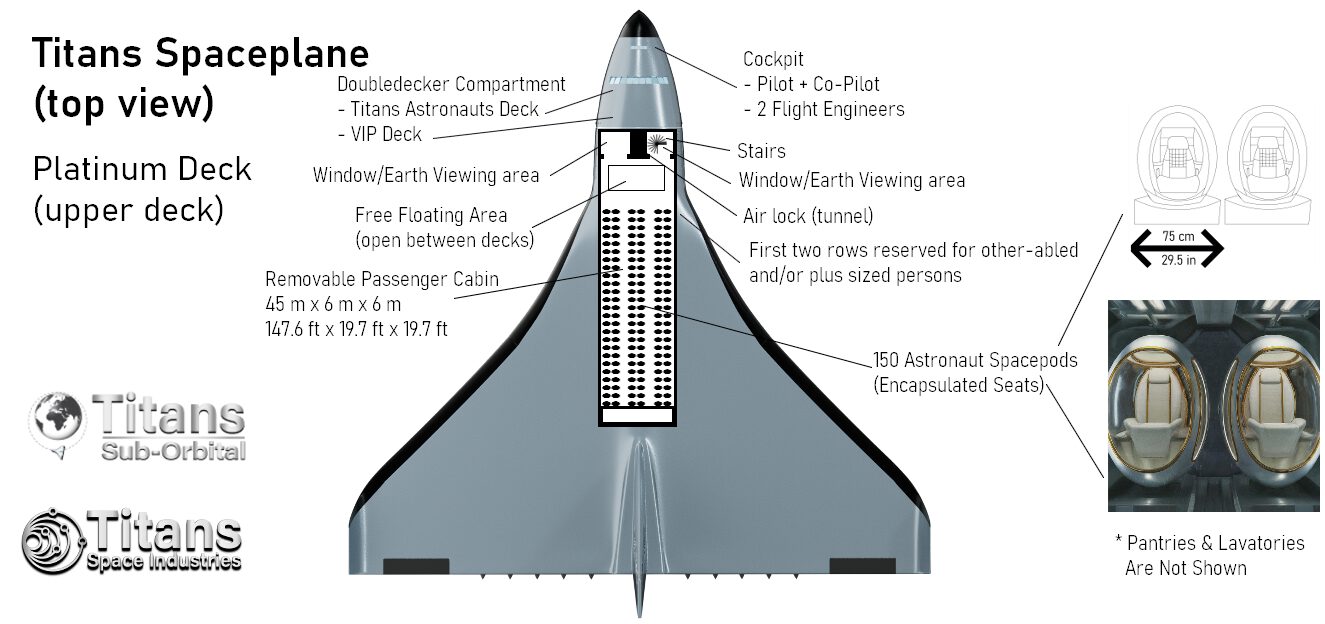
Titans Spaceplanes can operate from any (partnered) large airport, and it can carry up to 330 astronauts or a 90-100 ton payload into any 555-km (300 nmi, 344 mi) orbit; they use multi-cycle airbreather propulsion to reach the top of the troposphere and then ignite the rocket engines to reach Low-Earth Orbit.